
In this use case, you will learn about the common data challenges faced by large organizations and how Fairspace can help to address those challenges. Fairspace is an open-source solution developed by The Hyve in collaboration with Institut Curie, a cancer research hospital in Paris.
What is Fairspace?

Fairspace was created as a system to help research organizations achieve more flexible and FAIR research data management - securely storing and organizing their research data sets, sharing this data with collaborators, and easily searching for metadata and data (faceted search).
Fairspace lets researchers annotate their data collections with relevant metadata properties and link the data to associated metadata entities such as subjects, samples, and projects. This helps researchers retrieve their own data more easily, make it findable for others, and it contributes to implementation of the FAIR principles in practice. Fairspace ensures that all metadata entities have a unique identifier and checks metadata consistency and validity upon data entry.
Fairspace also allows organizations to customize the configured data model by specifying custom entity types and constraints. This enables the adoption of community standards for metadata relevant for the research domain and contributes to the reusability of the data.
Fairspace has its own file storage system and can connect to other storage systems. Keycloak is used for authentication and access management, which enables Fairspace to connect to institute login systems such as LDAP. Metadata is stored using the Resource Description Framework (RDF) standard.
The system is secure and scalable by design. Audit logging is done on file and record level. Organizing backups and restoring data after failure are relatively straightforward.
Data Management Challenges that needed to be solved
- Data is disconnected: it is difficult to find related data.
Researchers wanted to find relevant data, especially data related to a specific patient or sample or group of patients. It was impossible due to non-existing central indexes, missing metadata on the data ,common patient or sample identifiers, or a shared data model.
- Not being able to find available data relevant for a researcher, there is no overview.
Relevant data was hard to find because it was stored across many systems, in multiple locations and lacked a shared metadata catalog.
- Available data is difficult to access.
Researchers and data scientists could not access research data easily since it was stored in different - often not very well suited - places such as research laptops, lab hard drives, usb drives. It was not easy to share data with other research groups.
Data managers wanted to share data, but there was no system that supported convenient and secure data sharing.
- Research data is not always stored securely and reliably.
The organization wanted data to be stored securely to prevent data loss and to conform to policies and regulations. However, many research groups were still storing data in ad-hoc storages where appropriate access control or auditing are not ensured.
- The data storage and analysis environment were difficult to access and use.
Data scientists wanted an analysis environment with access to the data and with analysis tools and storage, but apparently, the KDI environment was not optimal for all researchers, and it was difficult to store data and add metadata in the existing data storage.
Institut Curie’s project objectives

The main user goals for Institute Curie were:
- Making data findable across research groups, and implementing easy filtering and browsing through data and metadata.
- Connecting all research data to institute level data (patients, samples).
- Enforcing strict access rules when accessing data - some research groups and researchers wanted to keep their data private.
- Collaboratively creating, modifying, analyzing and sharing files.
- Having a user-friendly interface with an existing biomedical data storage and metadata repository.
- Restricting metadata access for external collaborators.
How The Hyve approached the challenges and came up with Fairspace as a solution

One of the biggest challenges of the Fairspace project was to combine features required for a central data catalog with features needed for a dynamic working and collaboration environment. For example, different rules apply to data deposited for archiving purposes (immutable) and for active project data which groups are still collaborating on (mutable). As a consequence, the solution was found in a more complex data lifecycle. Data needed to be grouped into collections, follow a workflow with several statuses (active, read-only, archived, deleted) and different access modes (restricted, metadata published, metadata & data published).
An overview of the sample data flow:

How does Fairspace work?

Custom metadata model
Each knowledge domain requires different concepts and standards. That is why Fairspace uses a metadata model that data stewards can easily adjust.
Easy annotation
Data sets can be annotated and assigned a persistent identifier (PID) to create a semantic metadata store that contains information on all linked data sources and metadata.
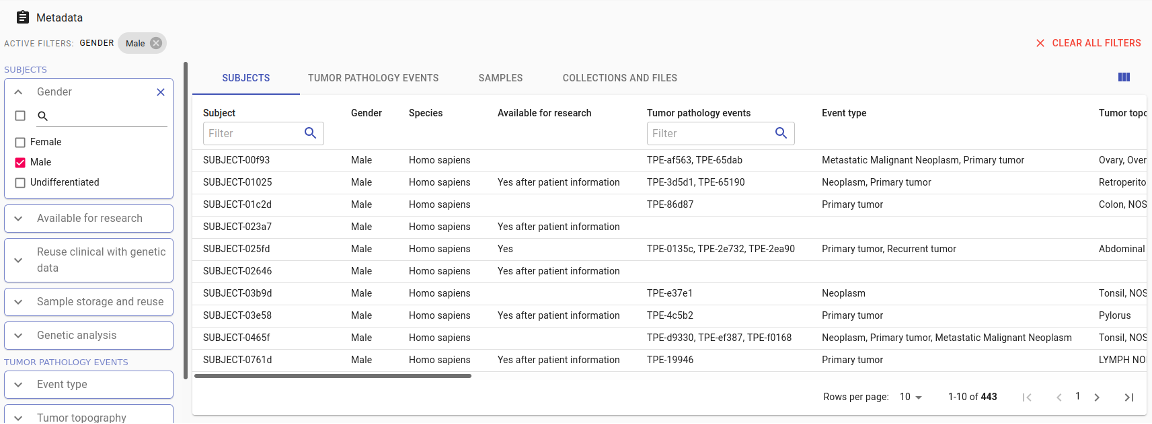
Intuitive search and browse
The semantic metadata store gives a clear overview of all data assets. The configurable user interface allows users to run queries with just a few mouse clicks.
Powerful analysis
Integration with JupyterHub allows for flexible analysis, query opportunities and automated addition of metadata to pipeline results.
Data sharing
Access can be specified per user, but also per workspace. Effective access per user depends also on collection status and current view mode.
Easy integration with External Storages
Fairspace has its own file storage system, but can also connect to other storage systems to enable access to data sets stored in external repositories. This integration uses WebDAV which is a standard file access protocol for the Web supported by many vendors.
Was the Fairspace project successful?
Fairspace has proven to be an easy-to-use open-source research data management tool that was able to resolve the data management challenges faced by Institut Curie. It also allowed them to make their research data more FAIR.
Institut Curie is currently in the process of implementing Fairspace in daily practice, starting with individual research groups. In time, it will be implemented across the entire organization.
You can find more in-depth information on how Fairspace works in the repository documentation.
If your organization is facing similar data management challenges and you are overwhelmed by the amount of closed source tools available, feel free to contact The Hyve. Our experts can discuss with you how to best tackle these issues within your R&D departments.